The Global Impact of Obesity
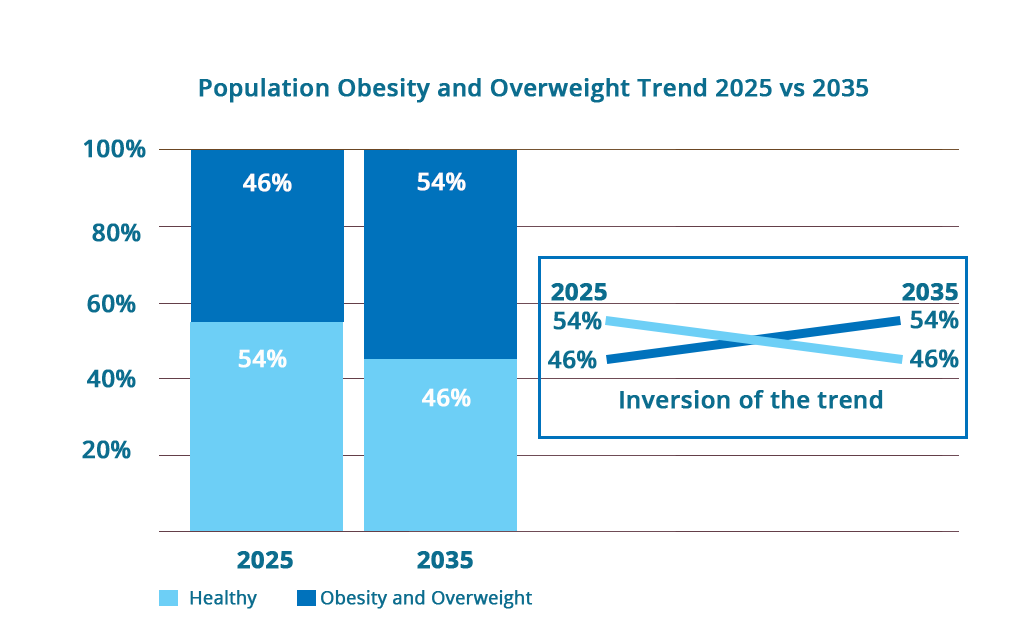
Obesity has become one of the most critical public health challenges worldwide. According to the World Obesity Federation, over 2.2 billion people were classified as overweight or obese in 2020, and this number is expected to rise dramatically in the coming years.
The impact of obesity extends far beyond individual health. It is a major contributor to non-communicable diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, and stroke. Additionally, obesity significantly increases healthcare costs, putting pressure on national economies. Studies estimate that global obesity-related healthcare costs will exceed $4 trillion annually by 2035.
Moreover, obesity is not just a problem in high-income countries. Many developing nations are experiencing a rapid rise in obesity rates due to urbanization, sedentary lifestyles, and increased access to processed foods. This shift is creating a double burden where malnutrition and obesity coexist.
Addressing obesity requires a multi-faceted approach, including government policies, public health campaigns, and individual lifestyle changes. Initiatives such as sugar taxes, improved food labeling, and increased physical activity programs have shown promising results in reducing obesity rates.
Ultimately, combating obesity is essential for global health, economic stability, and quality of life. By taking action now, we can mitigate its long-term consequences and create healthier societies.
